February 18, 2021. One of the important aspects of an institute in order to meet its goal is to harmonize its activities within its offices. A case in point is the BAFS wherein the common purpose is to develop the Philippine National Standards (PNS).
Standards and regulations are essential to ensure the health and safety of consumers. They also contribute to making products and services globally competitive.
As the sole standard-setting agency of the Department of Agriculture, BAFS is committed not only to develop Philippine National Standards (PNS) for the agri-fishery sector based on sound science, but also in ensuring that these standards are promoted and adopted as technical regulations by the DA regulatory agencies.
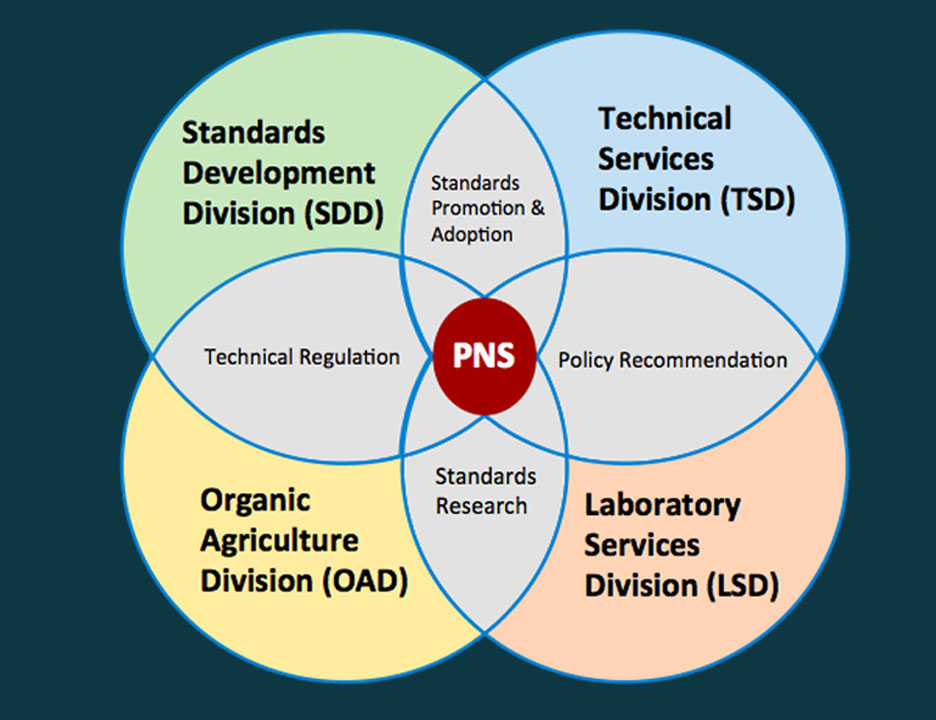
The BAFS has four (4) technical divisions, namely the Standards Development Division (SDD), Technical Services Division (TSD), Laboratory Services Division (LSD), and Organic Agriculture Division (OAD). The core function of the BAFS is the development of relevant PNS for the agri-fishery sector. The SDD’s main function is on the development of the PNS while TSD is responsible to promote and ensure the adoption of the PNS developed by the SDD. The LSD supports PNS development through standards research and management of an information system for all scientific data collected. Similarly, the OAD supports PNS adoption by translating PNS to relevant organic agriculture regulations (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Interrelationship of BAFS Divisions
The functions and interrelations among the four (4) technical divisions are presented in Table 1. The SDD develops the PNS for agriculture and fishery primary and post-harvest products, tools, machineries, equipment, and structures. The division ensures that these PNS are harmonized with relevant regional and international standards, consistent with the Philippines’ rights and obligations under bilateral and multilateral trade agreements and the Philippines’ commitments under regional and international economic cooperation. The SDD seeks scientific advice and data sources from the LSD for the development of PNS then endorses the approved PNS to the TSD for its subsequent promotion and to ensure their adoption by the regulatory agencies.
The LSD maintains a pool of scientific experts, who provides technical advice on food safety and organic agriculture related issues. At the request of the SDD, the LSD conducts risk profiling and/or risk assessment of relevant food/commodity-hazard combinations relevant to the agri-fishery sector. The LSD also collects scientific data to support PNS development and implementation of organic agriculture regulations while managing an information system for the collection and repository of all scientific data collected in relation to standards and organic agriculture regulations, including those from the DA regional integrated laboratories.
The TSD promotes the PNS developed by the SDD through the development of appropriate Knowledge Products and conduct of Learning and Development (L&D) activities. Likewise, this division has the following functions: a. Responsible for ensuring that the PNS are adopted by the relevant DA regulatory agencies (including the OAD for organic agriculture-related standards) as mandatory technical regulations or sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures; b. Provides policy recommendations to the DA regulatory agencies and SDD on the appropriate risk management options in the light of the results of the risk profiling and risk assessment conducted by the LSD; and c. Provides policy recommendations to the regulatory agencies, SDD, and OAD on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) issues (e.g. technical regulations, standards, conformity assessment) affecting the agri-fishery sector.
The OAD is the regulatory unit on organic agriculture in relation to registration of organic inputs/products and integrated farms and accreditation of organic certifying bodies both for the third-party certification system and Participatory Guarantee System (PGS). As part of its regulatory functions, OAD monitors compliance with organic agriculture regulations and seeks the support of SDD on the development of PNS and of the LSD on scientific data to fulfill its organic agriculture regulatory functions including the assistance of TSD to promote organic agriculture standards.
Table 1. Summary of BAFS’ four divisional functions and their interrelations:
| BAFS Division | Functions | Maintain Outputs | Interrelation with other Divisions |
| Standards Development Division (SDD) |
|
PNS |
To TSD - endorses PNS for promotion and adoption by relevant DA regulatory agencies From OA - develops PNS relevant to organic agriculture |
|
|
Monitor adoption of approved PNS into technical regulations or SPS measures Provide policy recommendations to DA regulatory agencies, OAD and SDD on both food safety and TBT issues |
Policy Recommendations |
To LSD - requests for scientific advice and reports on food safety issues To OAD - provides policy recommendations in relation to organic agriculture regulations |
|
|
|
Risk assessment report Research reports Information system |
From TSD - requests for food-hazard combination to be studied From OAD - requests for scientific data to be generated |
|
|
Conduct monitoring and surveillance to examine compliance with relevant OA agriculture regulations |
a. Certificates OA Policy Recommendations Organic Agriculture Registration System Organic Agriculture Accreditation System |
To TSD - requests for the promotion of organic agriculture standards To LSD - seeks scientific advice and data sources to support organic agriculture regulatory functions |
